In an era where the Bureau of Labor Statistics continues to report millions of unfilled job openings, the debate between inbound and outbound recruiting has shifted from “which is easier” to “which delivers a measurable return on investment (ROI).”
For high-growth companies and RPO providers, understanding the mechanical differences between these two strategies is the difference between a filled seat and a stagnant department. This guide dives into the data-backed execution strategies of both methods and provides a framework for when to deploy each.
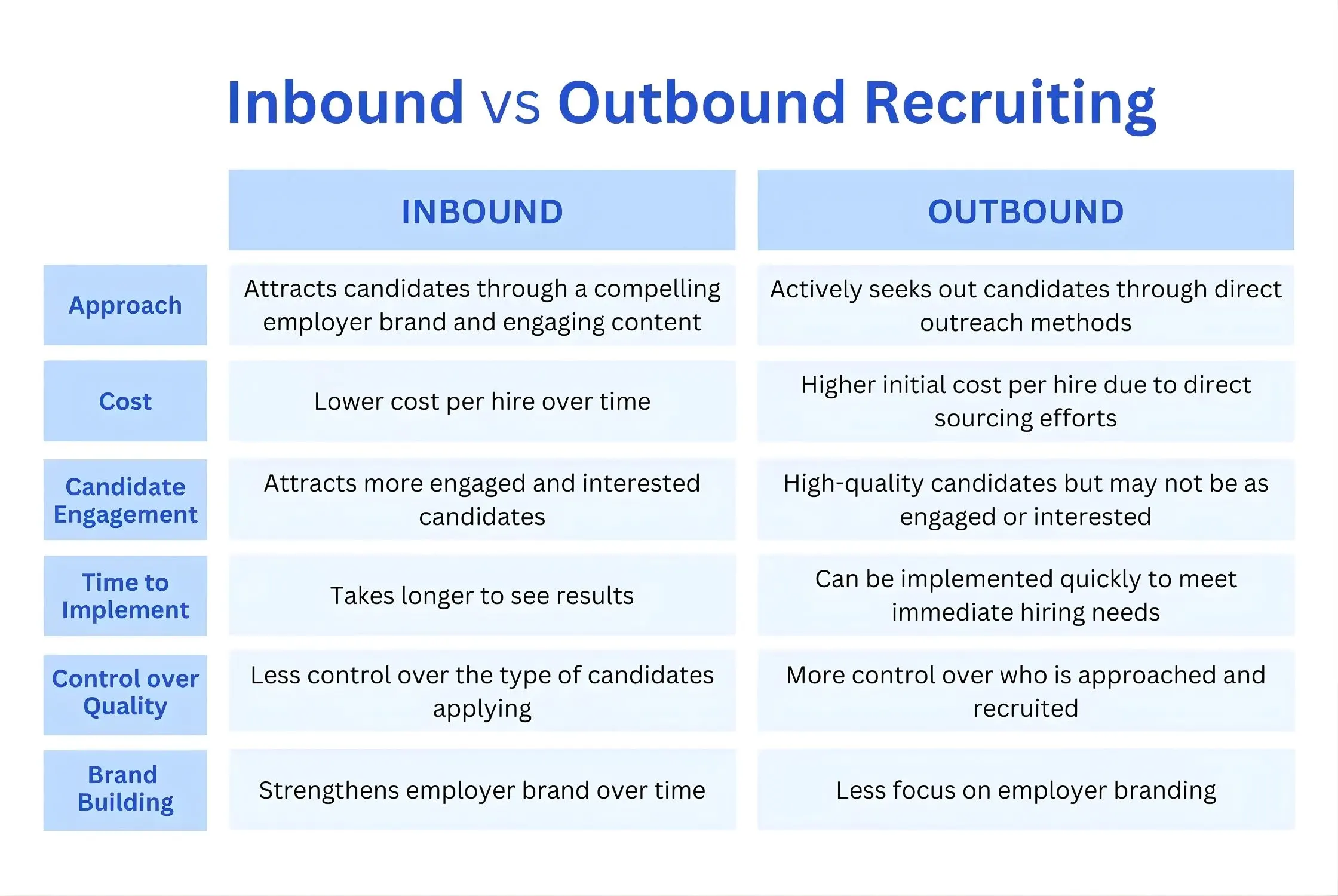
The Core Divergence: Active vs. Passive Talent
The fundamental difference lies in the candidate’s psychological state at the time of engagement.
- Inbound Recruiting relies on your “employer brand” to pull candidates toward you. It treats the job seeker as a consumer.
- Outbound Recruiting is a proactive “headhunting” model. According to Recruitee, roughly 70% of the global workforce is passive—meaning they are not actively looking at job boards. Outbound is the only way to reach this majority.
Inbound Recruiting: The “Long-Tail” ROI Strategy
Inbound recruiting is an investment in your company’s visibility. It involves content marketing, SEO-optimized career pages, and social media presence. Top talent is often off the market in as little as 10 days, meaning your inbound engine must not only attract quality but do so with incredible speed.
How it Works in Detail:
- Brand Magnetism: You create content that showcases your culture (e.g., “Day in the life” videos).
- Frictionless Application: Utilizing a high-performing Applicant Tracking System (ATS) to capture interest.
- Talent Pooling: Candidates who aren’t a fit today opt-in to your newsletter or talent community for future roles.
Inbound Recruiting Strategies
In today’s hyper-competitive landscape, speed is a primary differentiator. Research indicates that the most sought-after candidates are off the market within just 10 days of beginning their search. This reality creates a high-pressure environment where organizations must not only identify elite talent but engage them before the competition. To win the “war for talent,” your inbound engine must be optimized for both reach and rapid conversion.
1. Free Job Posting Sites
The default strategy for most recruiters involves leveraging free job listing sites to cast a wide net. Platforms like Indeed, LinkedIn, and Monster are essential for visibility. However, for a truly effective inbound plan, you must also utilize industry-specific platforms like Dice for tech or AngelList for the startup ecosystem. Ensure your job descriptions go beyond a list of requirements; focus on the work environment and personal growth opportunities to truly stand out.
2. SEO
If a candidate is searching Google for “web development jobs in Florida,” your career page needs to be the first thing they see. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a critical inbound tactic. By optimizing your website’s careers section for specific long-tail keywords, you ensure maximum discovery by active job seekers without paying for every click.
3. Content Marketing on Social Media
While blogs are excellent for building long-term authority, social media allows for rapid content distribution. Promoting your brand through consistent posts about open roles, employee wins, and work culture helps persuade quality candidates to apply. It turns your social channels into a living window of what life looks like at your company.
4. List your Jobs on Google for Job Search
Google for Jobs is often the first result a candidate sees. Ensuring your job openings are indexed correctly here is vital, especially for localized hiring. It captures high-intent traffic at the very moment they start their search, placing your brand front and center.
The ROI Metrics:
- Lower Cost Per Hire: Once the infrastructure is built, the cost to attract one additional candidate is nearly zero.
- Higher Cultural Alignment: Candidates who “self-select” into your brand after reading your content often have a higher retention rate. Glassdoor reports that a strong employer brand can reduce turnover by 28%.
Outbound Recruiting Strategies: A Mindset Shift
To be successful at outbound, you must view your open positions as “products” and candidates as “prospects.” Your pitch and your employer brand matter more here than anywhere else. This requires mastering the art of cold emailing and cold calling—not by spamming, but by crafting high-value, personalized messages that cut through the digital noise.
1. Subscribe to Candidate Repositories
Accessing massive candidate databases is one of the most popular outbound strategies. Platforms like LinkedIn, Indeed, and Monster offer paid recruiter subscriptions that provide a direct line to millions of profiles. However, keep in mind that these are “shared” pools; your competitors have access to the same data. The ROI comes from how you use Boolean search in recruitment to find the profiles everyone else misses.
2. Recruiting via Social Media
There has never been a better time to harness the power of social media. Beyond LinkedIn, platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and X (Twitter) allow you to find “interesting” candidates in their natural digital habitats. As a modern recruiter, these platforms are often the best place to uncover talent that hasn’t updated a traditional resume in years but remains highly active in their professional community.
3. Hunt for Passive Talent
As noted, roughly 70–75% of the entire workforce is “passive”—currently employed but open to the right opportunity. Hunting for this talent is a game-changing strategy. By reaching out to individuals who are already successful in their current roles, you ensure a higher quality of hire. This approach is especially productive for senior-level or managerial roles where the best candidates aren’t browsing job boards; they are busy leading teams elsewhere.
Strategic Comparison: When to Choose What?
| Feature | Inbound Recruiting | Outbound Recruiting |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Awareness & Pipeline Volume | Speed & Candidate Precision |
| Target Audience | Active Job Seekers | Passive Top-Tier Talent |
| Implementation | Career Sites, Social Media, Job Boards | Headhunting, LinkedIn Sourcing, Networking |
| ROI Horizon | Long-term (Brand Equity) | Immediate (Closing Roles) |
| Best For | High-volume roles (Junior to Mid-level) | Niche Technical & Executive Roles |
When to Use Inbound:
Use inbound for “evergreen” roles where you always need talent (e.g., Customer Support or Sales Associates). It is ideal for remote jobs where the applicant volume is naturally high. In fact, Datapeople suggests that for remote-first roles, inbound often outperforms outbound due to the massive global reach of modern job boards.
When to Use Outbound:
Use outbound for roles where the talent pool is shallow. If you need a Lead Developer or a specialized CFO, they are likely already employed and being treated well. You must “hunt” them. This is the core of modern RPO trends for 2025, where agencies are increasingly hired for their outbound “hunter” capabilities rather than their administrative skills.
The Hybrid Approach: The “Total Talent” Model
The highest ROI is achieved by a hybrid model. Use Inbound to build a constant “warm” pool of talent and Outbound to fill specific, high-stakes gaps.
To execute this effectively, your team needs a specific set of recruiting skills, balancing the marketing-savviness of inbound with the sales-tenacity of outbound. By mastering the full-cycle recruiting process, you ensure that regardless of the source, the candidate experience remains elite.
Final Verdict
- Better ROI for Budget: Inbound.
- Better ROI for Growth/Speed: Outbound.
Most companies fail at outbound because it requires dedicated time that internal HR teams often don’t have. This is why outsourcing to a partner who understands both “pull” and “push” strategies is often the most cost-effective move.
Ready to optimize your sourcing strategy? Contact Redirecruit today and let us build a custom outbound engine for your growth.

